Neutralisation reactions
This type of chemical reaction is restricted to a particular class of compounds viz. acids and alkalies or acids and bases. The neutralization reactions, in a way, are laso double decomposition reactions. Let us consider following few examples.
1. Take 10 ml of a dilute solution ( say 0.1N) of sodium hydroxide in a conical flask. Add two drops of methyl orange indicator to it. The colour of the solution becomes yellow. From a burette, add drop by drop a dilute solution ( say 0.1N ) of hydrochloric acid to it. Shake the conical flask continuously during the addition of HCl. At one stage, the solution in the conical flask becomes orange. Stop the addition of hydrochloric acid now. Check the orange solution in the conical flask with the help of blue and red litmus paper. There is no effect on any litmus paper. This shows that the solution in the conical flask is neutral. Hydrochloric acid belongs to the class of acids. Sodium hydroxide belongs to the class of bases or alkalies. So this chemical reaction is an acid –alkali (or acid –base) reaction. Since it results in neutralization of both, acid and base, it is called a neutralization reaction. The following figure shows acid –base neutralization.
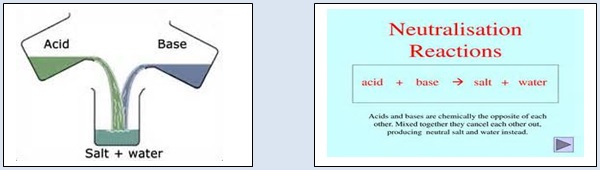
2. Take 10 ml of a dilute solution ( say 0.1N) of sodium carbonate by a pipette in a conical flask. Add two drops of methyl orange indicator to it. The colour of the solution becomes yellow. From a burette add drop by drop a dilute solution ( say 0.1N) of sulphuric acid to it. Shake the flask. At one stage, the solution in the conical flask becomes orange. Stop the addition of sulphuric acid solution now. Check the orange solution with the help of blue and red litmus paper. There is no effect on any litmus paper. This shows that the solution in the conical flask is neutral. Sulphuric acid belongs to the class of acids. Sodium carbonate belongs to the class of bases or alkalies So this chemical reaction is an acid –alkali (or acid–base) reaction. It is a neutralization reaction.
In the above reactions, an acid reacts with a base or alkali to form salt and water.
A chemical reaction in which an acid reacts with a base (or alkali) to form salt and water in aqueous medium is called a neutralization reaction.
Salts are prepared by the reaction between an acid and a base. A particular salt can be prepared by choosing a proper acid and a proper base. For example, copper sulphate can be prepared by the reaction between copper oxide or hydroxide and sulphuric acid. Potassium nitrate can be prepared by the reaction between potassium hydroxide and nitric acid. The concept of neutralization of an acid by a base finds many applications. One such application is described below.
Hydrochloric acid is produced in the stomach and is used in the digestion of proteins in a human body. If extra acid is produced or if the acid produced remains unutilized, it gives burning sensation to the person. This may lead to ulcer. To get rid of this ailment, the principle of neutralization is used to control the acidity in the stomach. The person suffering from acidity is advised to take a tablet or liquid containing a base or alkali. The tablet or liquid –milk of magnesia (magnesium hydroxide) that neutralizes the acidity and gives relief to the patient.
Some more examples of neutralization reactions are given below.
1. KOH + CH3COOH → CH3COOK + H2O
2. NH4OH + HCl → NH4Cl + H2O
3. Ca(OH)2 + 2 HNO3 → Ca(NO3)2 +2 H2O
4. H2 C2 O4 +2 NaOH → Na2 C2 O4 + 2 H2O
