Decomposition reactions
Let us discuss following few examples.
1. Take a little amount of lead nitrate in a hard glass tube. It is a white powder. Heat the hard glass tube slowly. Reddish brown fumes are evolved. The compound lead nitrate breaks up into simpler substances – solid lead oxide, nitrogen dioxide gas and oxygen gas. The reddish brown fumes are due to nitrogen dioxide gas. Following figure shows the decomposition of lead nitrate.
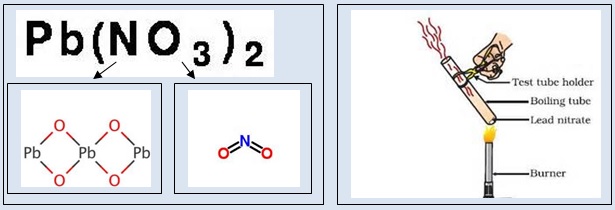
2. Take a pinch of manganese dioxide in a hard glass tube. Add about 10 ml hydrogen peroxide to it. Immediately small bubbles are seen in the hard glass tube. Oxygen gas is evolved. Hold a burning match stick at the mouth of hard glass tube. It burns more vigorously. Hydrogen peroxide breaks up into simpler substances –water and oxygen gas at room temperature. The ignited match stick burns more vigorously due to supply of oxygen gas. Magnesium dioxide does not take part in the reaction. It acts as a catalyst. It hastens the splitting of hydrogen peroxide.
3. Take about 2 grams solid potassium chlorate in a hard glass tube. Add about 0.5 grams of manganese dioxide to it. Heat the hard glass tube slowly. Hold a glowing splinter at the mouth of the tube. The splinter glows more intensely. Solid potassium chlorate breaks up into simpler substances –solid potassium chloride and gaseous oxygen. The splinter glows more intensely due to supply of oxygen gas. Manganese dioxide does not take part in the reaction. It acts as a catalyst. It lowers the temperature and increases the speed of the reaction.
In the above examples, one substance breaks up into two or more simpler substances.
A chemical reaction in which a substance breaks up into two or more simpler substances is called a decomposition reaction.
In the decomposition reactions, oxygen or nitrogen gas of the air does not take part in the reaction. Decomposition reaction is opposite of combination reaction. Decomposition reactions are, sometimes, further specified on the basis of the agency used for the decomposition process. For example, when electric current is passed through acidulated water, then water breaks up into simpler substances –hydrogen and oxygen gas. Since this decomposition is brought about by electrical energy, it is known as electrolytic decomposition or electrolysis. When mercuric oxide is heated, it breaks up into simpler substances –mercury and oxygen gas. This decomposition is brought about by heat. So it is called thermal decomposition. When silver bromide is exposed to sunlight, it breaks up into simpler substances –metallic silver and bromine vapour. This decomposition is brought about by light. So it is called photo decomposition.
Some more examples of decomposition reactions are given below.
1. PCl5 → PCl3 + Cl2
2. (NH4)2 Cr2 O7 → Cr2 O3 + N2 + 4H2O
3. 2Cu (NO3)2 → 2CuO + 4NO2 + O2
4. (NH4)2CO3 → 2NH3 + H2O + CO2
