Displacement reactions
Let us consider following few examples.
1. Take about 50 ml water in a beaker. Add 5 grams copper sulphate to it. Stir the solution well. The solution becomes blue. Transfer some of this solution in a test tube. Tie two iron nails with a thread and immerse them carefully in the copper sulphate solution in the test tube. Keep the test tube undisturbed for about half an hour. The blue colour of the solution slowly fades away and finally it becomes pale green. Take out the iron nails from the copper sulphate solution. The iron nails get a shiny coat of reddish brown copper metal on their surface. Here iron displaces copper from copper sulphate solution forming soluble copper sulphate and solid copper. Following figure shows a reaction between copper sulphate and iron nails
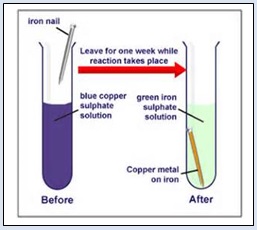
In this reaction, a more active element (Fe) displaces a less active element (Cu) from its salt solution.
2. Take a few granules of zinc in a test tube. Add about 10 ml dilute sulphuric acid to it. Heat the test tube for a minute. Bubbles of a gas come out. Take a burning candle near the mouth of the test tube. A pop sound is heard indicating the ignition of hydrogen gas. Here zinc displaces hydrogen from sulphuric acid forming soluble zinc sulphate and gaseous hydrogen.
In this reaction, a more active element (Zn) displaces a less active element (H) from its solution.
3. Take a magnesium ribbon and put it in a copper sulphate solution taken in a beaker. Keep the beaker undisturbed for half an hour. The blue colour of copper sulphate solution slowly fades away and finally, the solution becomes colorless. The magnesium ribbon gets a shiny coat of reddish brown copper metal on its surface. Here magnesium displaces copper from copper sulphate solution forming soluble magnesium sulphate and solid copper.
In this reaction, a more active element ( Mg ) displaces a less active element ( Cu ) from its salt solution.
Based on the above described and similar experiments, one can list the elements in the order of their decreasing chemical reactivity. A series formed in this manner is called activity series. Such a series of metals is given below.
In all the above examples, a more reactive element displaces a less reactive element from its solution.
A chemical reaction in which a more reactive element displaces a less reactive element from its solution is called a displacement reaction.
K > Na > Mg > Al > Zn > Fe > Pb > Cu > Ag > Au Some more displacement reactions are given below.
1. Cl2 + 2 KI → 2 KCl + I2
2. Cu + 2 AgNO3 → Cu(NO3)2 + 2 Ag
3. Zn + FeSO4 → ZnSO4 + Fe
4. Zn + CuSO4 → ZnSO4 + Cu
