Cell structure
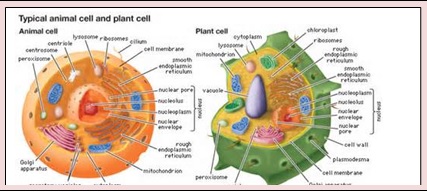
A Cell when seen under a simple microscope appears to have a centrally placed nucleus and cytoplasm around it. The living component of the cell is called ‘protoplasm’. Cells when observed under electron microscope show that cells internally are made up of organelles. Organelles are membranous structures and have a specific shape and defined functions. The important cell organelles are cell membrane, cell wall, cytoplasm, mitochondria, Golgi bodies, ribosomes, lysosomes, plastid, nucleus and vacuoles. Let us learn more about them.
1. The cell membrane: the outermost covering of the cell is the cell wall. It is thin and flexible. The membrane protects the cell. It also helps the transport of the materials in and outside the cell.
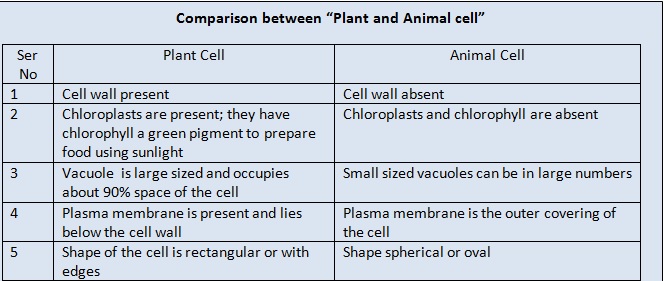
2. The Cell wall: It is a protective covering found in cells. The covering is made up of cellulose and hemi cellulose. The cell wall gives rigidity and strength to the cell. The rigidity to the plant is due to its cell wall.
3. Nucleus: the nucleus is usually centrally placed large oval or round structure. It is a membrane bound structure. The membrane is porous. It controls and co-ordinates the activities that take place in the cell (like the controller). The nucleus has hereditary material DNA in the form of chromosomes at the time of cell division. The hereditary characters are carried forward in the chromosomes.
5. Cytoplasm: it is a liquid material that fills up the cell. It has all necessary materials needed for the cell. Various ions, proteins, enzymes, etc, are present in this component.
6. Mitochondria: these are primarily tubular in shape. Mitochondria has two membrane s. the inner membrane is folded. This is because it is larger than the outer one. This folding is a site of production of enzymes needed for energy requirements. ATP Synthesis is done in the mitochondria. These are also known as the power houses of the cells.
7. Golgi bodies: These are stacks of membrane bound sacs. These are present towards the periphery of the cell. They are concerned with storage of enzymes. They also help in transport of certain materials such as proteins outside the cell.
8. Vacuole: Vacuoles are an empty space. This space is larger in plant cells than the animal cells. Vacuoles are useful in storage of excretory products or in storage of temporary products. The large size of the vacuole in plant cells displaces the nucleus to one side.